|
Dataset Information
| Accession |
GSE243442
|
| Status |
2024/12/10 |
| Title |
Integrative biology of patients acutely infected with yellow fever virus |
| Organism |
Homo sapiens |
| Experiment type |
Expression profiling by high throughput sequencing |
| Summary |
Yellow fever (YF) is a life-threatening mosquito-borne disease prevalent in South America and Africa, accounting for up to 60,000 annual deaths. Between December 2016 and May 2018, Brazil reported its worst YF outbreak this century with a fatality rate of 33.6%. While YF vaccines have shown protective capabilities, the genetic profile of those infected with the wild-type YF virus (YFV) remains uncharacterized. Building on recent findings by Kallas et al. (2019), which discerned clinical and immunological determinants of YF mortality, we conducted a comprehensive transcriptional profiling of blood samples from YFV-infected patients. Our investigation integrated omics data with clinical and immunological metrics, contrasting the wild-type YFV acute infection signature against the response triggered by the YF17D vaccine strain and the signature linked to severe COVID-19. Our analyses revealed key molecular mechanisms of YFV infection and determinants of disease severity. Notably, a comparative assessment elucidated distinct gene expression patterns between wild-type YFV infections, YF17D vaccination, and severe COVID-19. This study offers pivotal insights into the molecular underpinnings of YFV infection and its severity, potentially enhancing our comprehension of viral infections at large. |
| Samples |
| GSM ID |
Sample info |
Characteristics |
Description |
|
GSM7785677
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR282.18 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785678
|
PBMC, Control, BSR281.32 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785679
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR280.13 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785680
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR279.61 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785681
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR278.51 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785682
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR277.9 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785683
|
PBMC, Control, BSR276.21 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785684
|
PBMC, Control, BSR275.33 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785685
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR274.55 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785686
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR273.34 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785687
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR272.11 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785688
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR271.5 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785689
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR270.7 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785690
|
PBMC, Control, BSR269.27 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785691
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR268.8 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785692
|
PBMC, Control, BSR266.64 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785693
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR265.4 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785672
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR287.49 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785694
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR264.50 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785673
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR286.53 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785695
|
PBMC, Control, BSR263.23 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785696
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR262.56 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785674
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR285.47 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785675
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR284.48 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785697
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR261.3 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785698
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR260.45 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785676
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR283.54 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785704
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR254.62 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785701
|
PBMC, Control, BSR257.22 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785705
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR253.19 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785708
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR250.2 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785709
|
PBMC, Control, BSR249.25 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785711
|
PBMC, Control, BSR247.66 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785712
|
PBMC, Control, BSR246.24 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785710
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR248.60 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785713
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR245.46 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785714
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR244.10 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785715
|
PBMC, Control, BSR242.65 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785716
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR241.59 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785717
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR240.17 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785718
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR239.12 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785719
|
PBMC, Control, BSR237.26 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785720
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR236.43 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785725
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR231.44 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785721
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR235.52 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785722
|
PBMC, Control, BSR234.29 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785726
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR230.42 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785723
|
PBMC, Control, BSR233.28 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Control |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785724
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR232.58 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785702
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR256.57 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785706
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR252.1 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785703
|
PBMC, Acute Survivor, BSR255.6 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785707
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR251.16 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785699
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR259.20 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
GSM7785700
|
PBMC, Acute Non-survivor, BSR258.15 |
tissue:PBMC; treatment:Acute_Non-survivor |
RNA from PBMCs was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), quantified using Nanodrop ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and integrity checked in a 2200 TapeStation system using RNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The cDNA libraries were constructed using the QuantSeq 3' mRNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina FWD (Lexogen GmbH, Austria), following the manufacturer's protocol. The concentration and the median size of the libraries were assessed by 2200 TapeStation with a DNA1000 ScreenTape (Agilent). The final pool of libraries was quantified by qPCR using the Kapa Sybr Green qPCR Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) and subjected to a single-end sequencing (75 bp) in a NextSeq 500 Sequencing with NextSeq 500/550 High Output Kit v2.5 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Raw single-end reads were preprocessed for quality control. Sequencing quality was assessed before and after adapter trimming using the program FastQC (Andrews 2010). The Trimmomatic software version 0.39 (Bolger, Lohse, and Usadel 2014) was used to remove adapters sequence trimming the 5, and 3 ends with a mean quality score below 25 (Phred+33) and discard reads shorter than 36 bp after trimming. We used the parameters LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:36. After preprocessing, the high-quality reads were mapped into the reference genome Homo sapiens (version GRCh38) with the bowtie2 program (version 2.2.5) (Langmead and Salzberg 2012). To quantify the gene abundance of the mapped reads in each sample, we used the featureCounts tool from the R/Bioconductor package Rsubread (Liao, Smyth, and Shi 2019) with the following parameters: GTF.featureType = gene, GTF.attrType = gene_id, isPairedEnd = FALSE, minOverlap = value 1, allowMultiOverlap = FALSE, countMultiMappingReads = FALSE. Normalization of the gene counts was performed with counts per million normalization (CPM) and quantile normalization, which accounts for differences in library size. |
|
| Platform |
GPL18573 : Illumina NextSeq 500 (Homo sapiens) |
| Literature |
39639628 |
| Download |
Download xCell Data Download Expression Analysis Data
|
|
xCell Plot
|
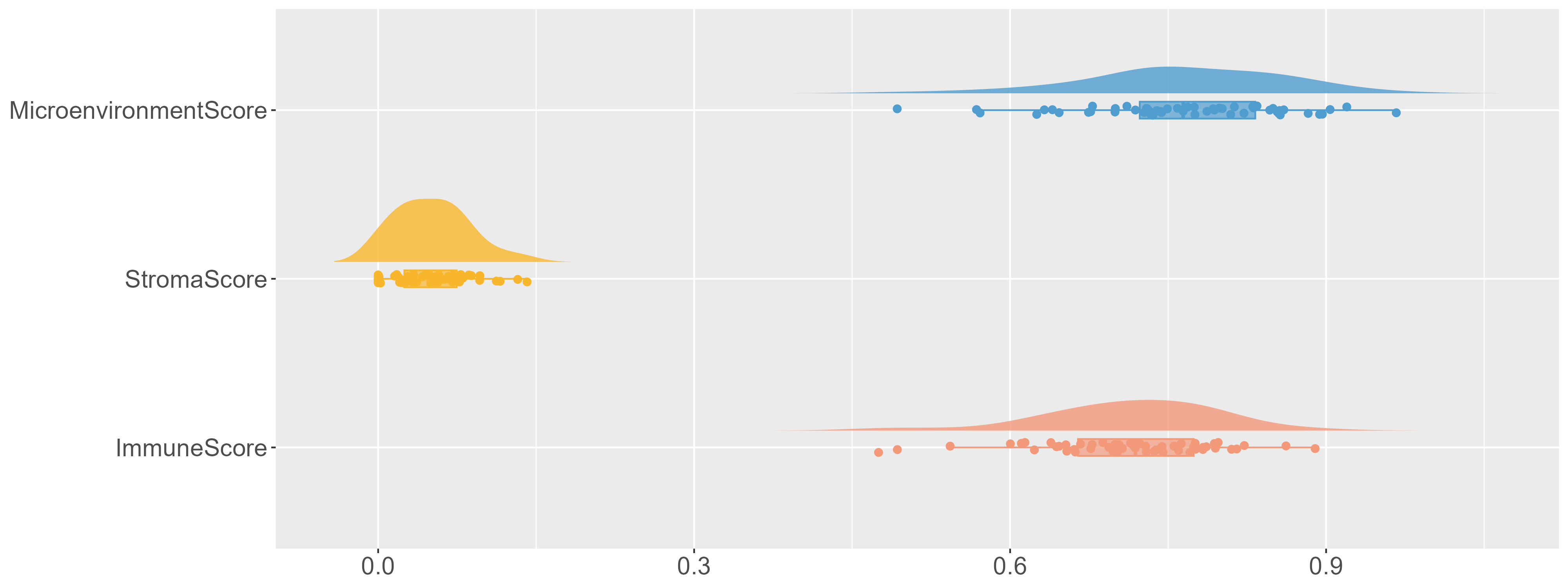
|
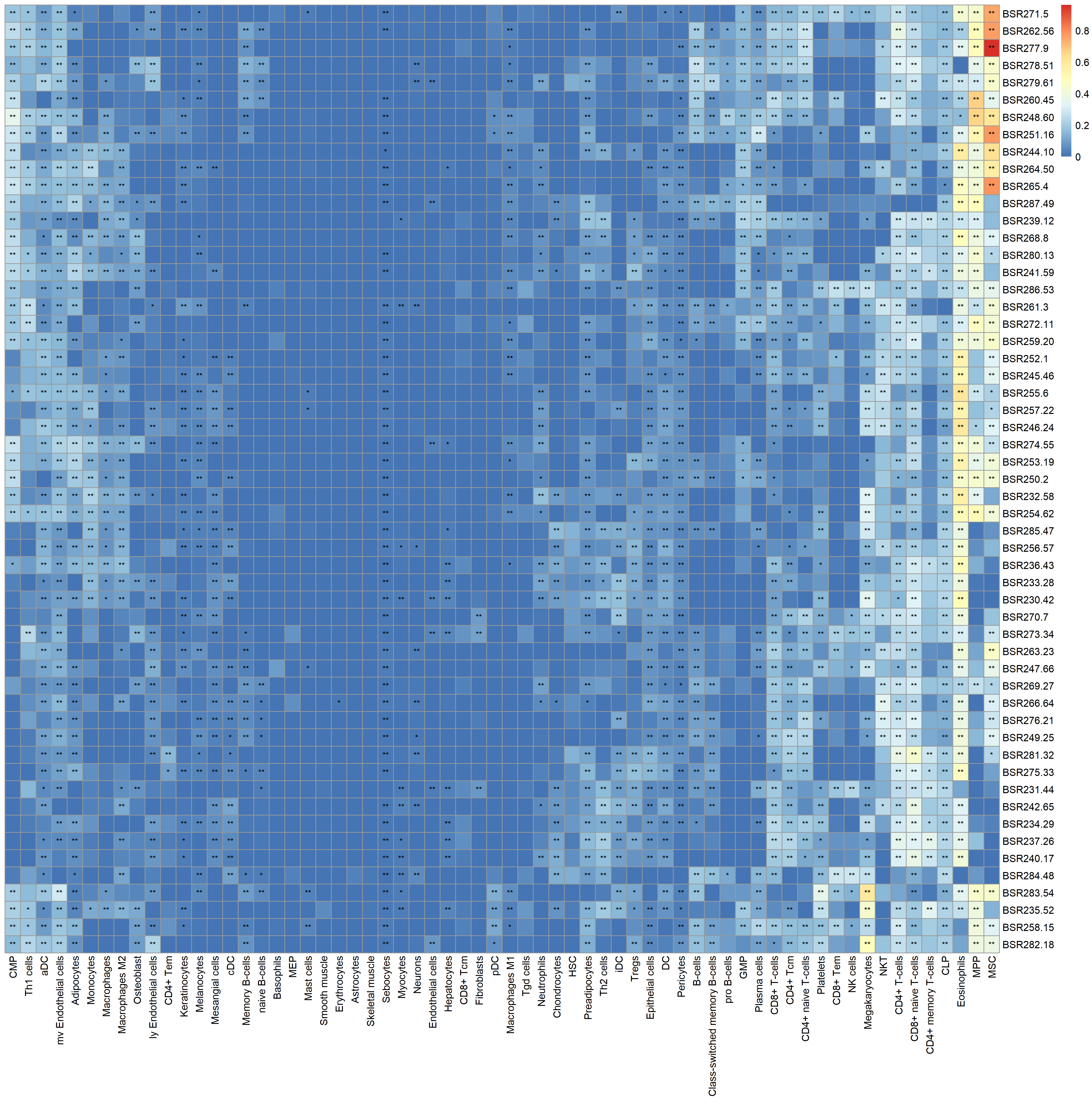 * p<0.05 ** p<0.01
* p<0.05 ** p<0.01
|
|
 Virus Dataset Detail
Virus Dataset Detail