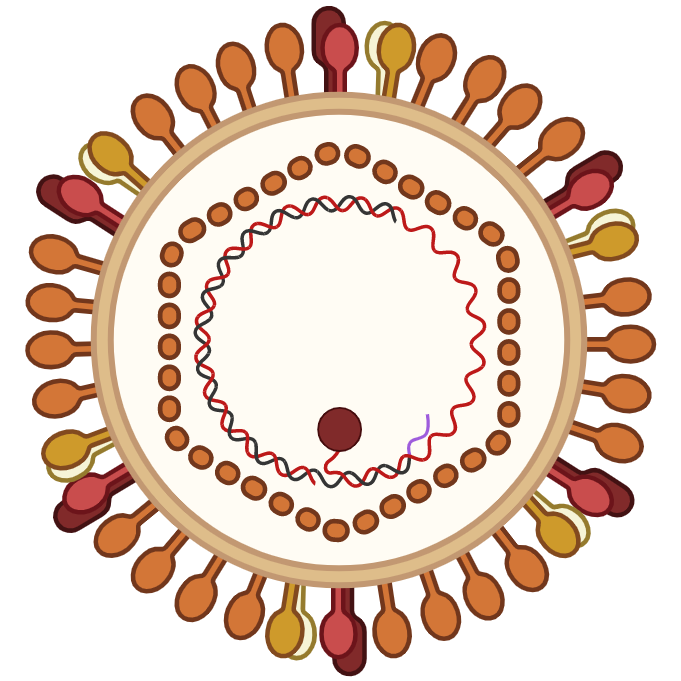
 Hepatitis B Virus
(HBV) Hepatitis B Virus
(HBV)
M
I
|
3.2kb
|
Artverviricota
Blubervirales
Hepadnaviridae
Orthohepadnavirus
Hepatitis B virus
|
HBV is a partially double-stranded DNA virus that primarily infects hepatocytes. It causes acute and chronic hepatitis, with chronic infection leading to severe complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Transmission occurs via blood and bodily fluids. The virus replicates via reverse transcription and integrates into host DNA.
|
Detail
|
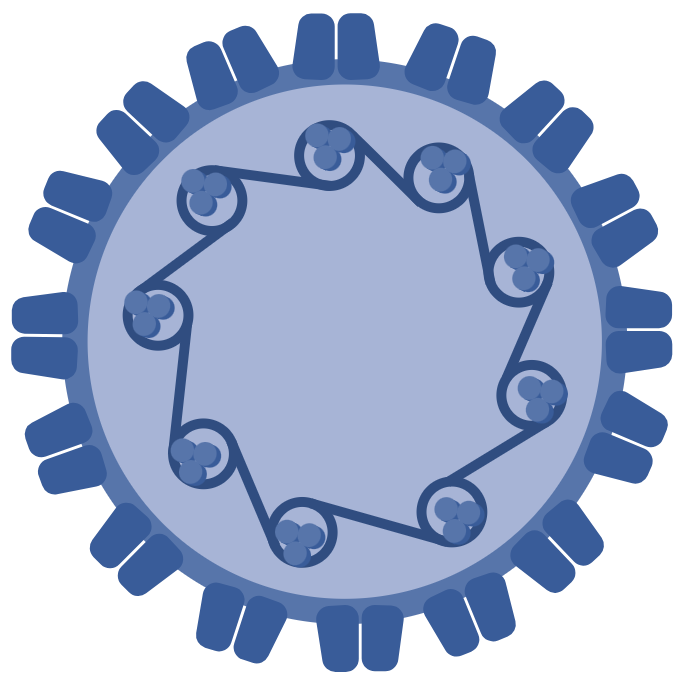 Human Papillomavirus
(HPV) Human Papillomavirus
(HPV)
M
I
|
8kb
|
Papillomaviricota
Sepolyvirales
Papillomaviridae
Alphapapillomavirus
Human papillomavirus
|
HPV is a small double-stranded circular DNA virus with a genome of approximately 8000 base pairs. The HPV life cycle strictly follows the differentiation program of the host keratinocyte. It is thought that the HPV virion infects epithelial tissues through micro-abrasions, whereby the virion associates with putative receptors such as alpha integrins, laminins, and annexin A2 leading to the entry of the virions into basal epithelial cells through clathrin-mediated endocytosis and/or caveolin-mediated endocytosis depending on the type of HPV.
|
Detail
|
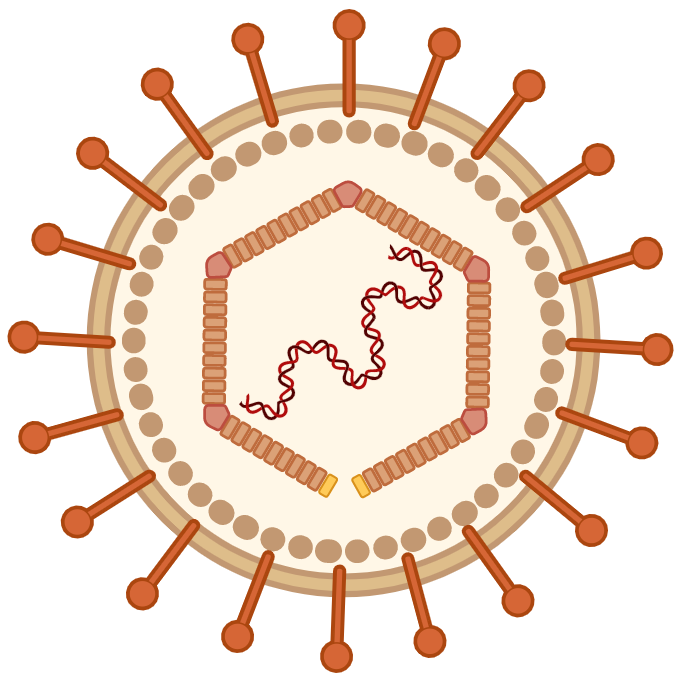 Epstein-Barr Virus
(EBV) Epstein-Barr Virus
(EBV)
M
I
|
172kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Lymphocryptovirus
Human gammaherpesvirus 4
|
EBV is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus and is the first identified oncogenic virus, or a virus that can cause cancer.
|
Detail
|
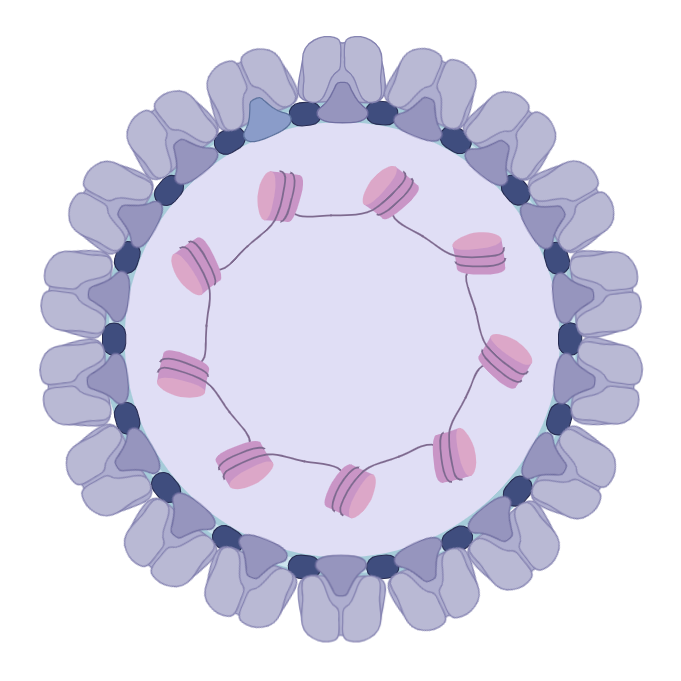 Merkel Cell Polyomavirus
(MCV) Merkel Cell Polyomavirus
(MCV)
M
I
|
5.4kb
|
Shotokuvirae
Sepolyvirales
Polyomaviridae
Alphapolyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus
|
MCV was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called digital transcriptome subtraction. MCV is one of seven currently known human oncoviruses. It is suspected to cause the majority of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer.
|
Detail
|
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus
(HIV) Human Immunodeficiency Virus
(HIV)
M
I
|
9.8kb
|
Artverviricota
Ortervirales
Retroviridae
Lentivirus
Human immunodeficiency virus 1/2
|
HIV are two species of Lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans.Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive.
|
Detail
|
 Human T-lymphotropic Virus 1
(HTLV1) Human T-lymphotropic Virus 1
(HTLV1)
M
I
|
9kb
|
Artverviricota
Ortervirales
Retroviridae
Deltaretrovirus
Primate T-lymphotropic virus 1
|
HTLV1 is a retrovirus of the human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) family. The most well characterized are adult T-cell lymphoma (ATL) and HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/Tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP), both of which are only diagnosed in individuals testing positive to HTLV-1 infection.
|
Detail
|
 Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus
(XMRV) Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus
(XMRV)
M
I
|
8.3kb
|
Artverviricota
Ortervirales
Retroviridae
Gammaretrovirus
Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus
|
XMRV is a gammaretrovirus linked to prostate carcinoma and chronic fatigue syndrome.
|
Detail
|
 Influenza Virus
(IV) Influenza Virus
(IV)
M
|
A:13.5kb
B:14.6kb
C:12.9kb
D:12.9-13.3kb
|
Negarnaviricota
Articulavirales
Orthomyxoviridae
Alphainfluenzavirus
Betainfluenzavirus
Gammainfluenzavirus
Deltainfluenzavirus
Alphainfluenzavirus
Betainfluenzavirus
Gammainfluenzavirus
Deltainfluenzavirus
|
IV virion is pleomorphic; the viral envelope can occur in spherical and filamentous forms. There are four genera of influenza virus, each containing only a single species, or type. Influenza A and C infect a variety of species (including humans), while influenza B almost exclusively infects humans, and influenza D infects cattle and pigs.
|
Detail
|
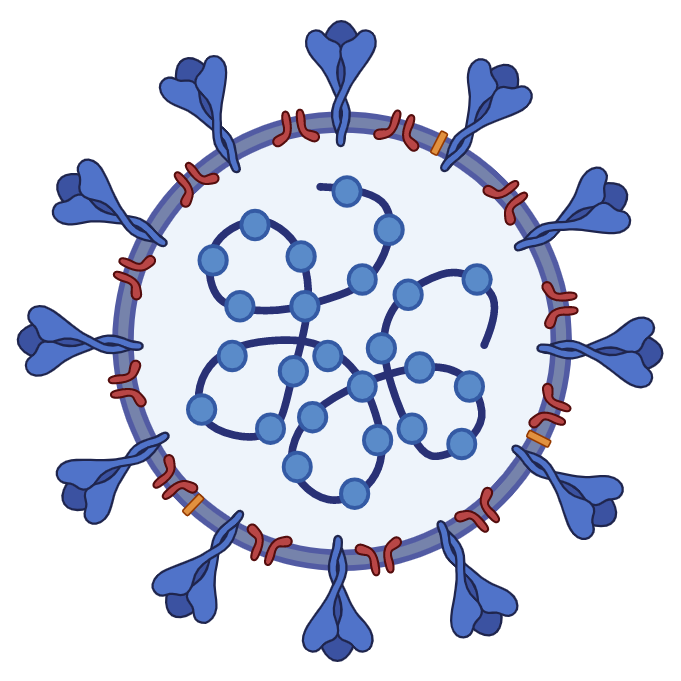 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2)
M
|
30kb
|
Pisuviricota
Nidovirales
Coronaviridae
Betacoronavirus
Betacoronavirus pandemicum
|
SARS-CoV-2 is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
|
Detail
|
 Herpes Simplex Virus 1
(HSV1) Herpes Simplex Virus 1
(HSV1)
M
|
152kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Simplexvirus
Simplexvirus humanalpha1
|
HSV1 infects humans, most often as cold sores. It is very common and contagious; about 67% of the world population under the age of 50 has Herpes simplex virus 1.
|
Detail
|
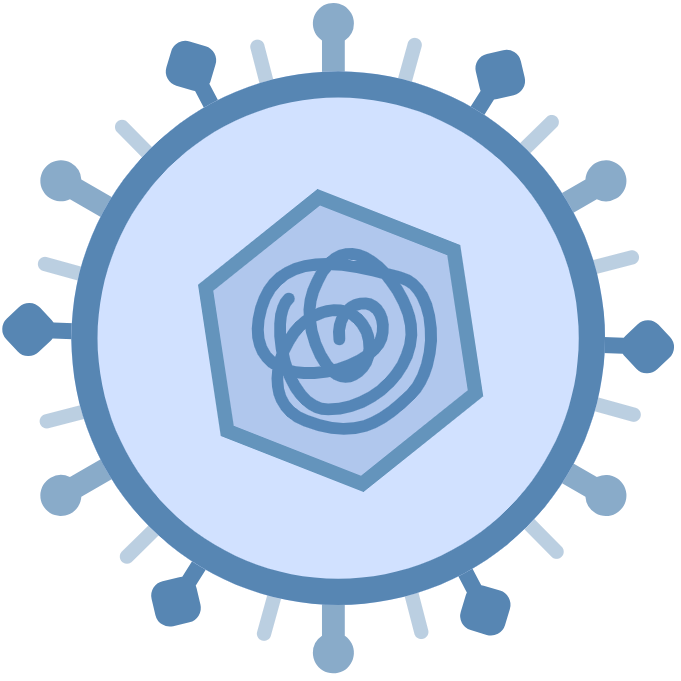 Herpes Simplex Virus 2
(HSV2) Herpes Simplex Virus 2
(HSV2)
M
|
155kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Simplexvirus
Simplexvirus humanalpha2
|
HSV2 most often as genital herpes. In the United States more than one in six people have the virus. It is primarily a sexually transmitted infection. Herpes simplex virus 2 tends to reside in the sacral ganglia. Herpes simplex virus 2 is periodically shed in the human genital tract, most often asymptomatically.
|
Detail
|
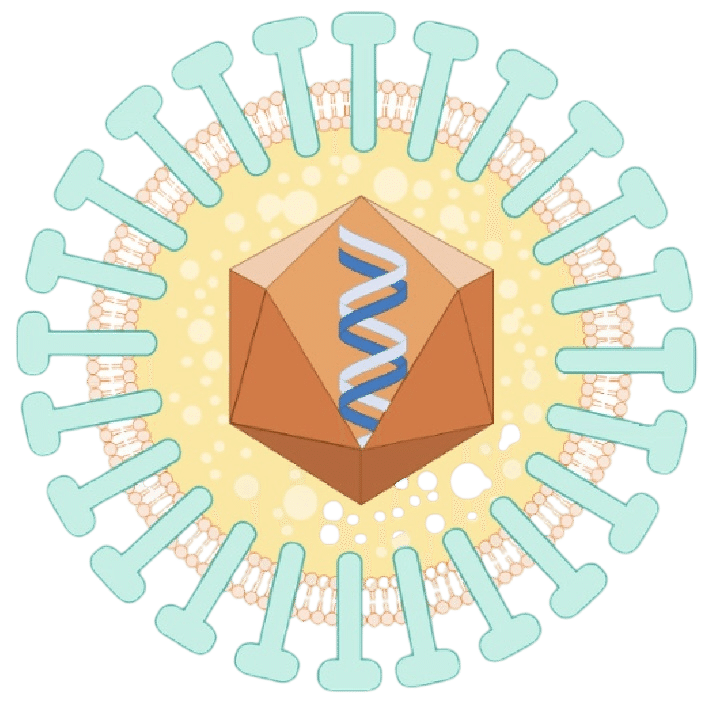 Human Cytomegalovirus
(HCMV) Human Cytomegalovirus
(HCMV)
M
|
236kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Cytomegalovirus
Human betaherpesvirus 5
|
HCMV also called human herpesvirus 5 (HHV-5), is a species of virus in the genus Cytomegalovirus, which in turn is a member of the viral family known as Herpesviridae or herpesviruses. It is also commonly called CMV. CMV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
|
Detail
|
 Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus
(KSHV) Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus
(KSHV)
M
|
165kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Rhadinovirus
Rhadinovirus humangamma8
|
KSHV is the ninth known human herpesvirus. It is also called Human herpesvirus 8, or HHV-8 in short. This virus causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer commonly occurring in AIDS patients, as well as primary effusion lymphoma, HHV-8-associated multicentric Castleman's disease and KSHV inflammatory cytokine syndrome.
|
Detail
|
 Varicella-Zoster Virus
(VZV) Varicella-Zoster Virus
(VZV)
M
|
125kb
|
Peploviricota
Herpesvirales
Orthoherpesviridae
Varicellovirus
Varicellovirus humanalpha3
|
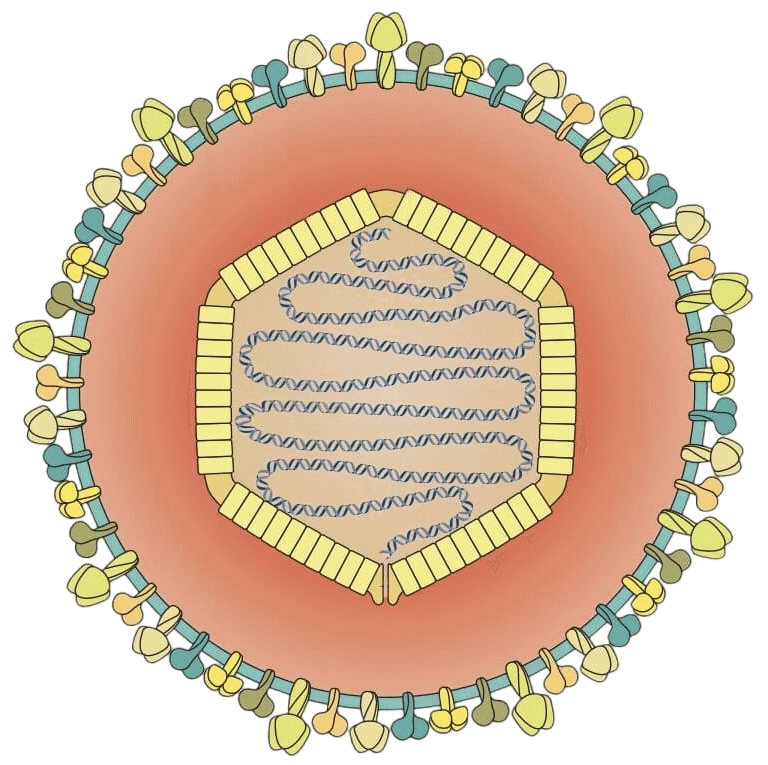
VZV also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zoster) in adults but rarely in children.
|
Detail
|
 Hepatitis A Virus
(HAV) Hepatitis A Virus
(HAV)
M
|
7.5kb
|
Pisuviricota
Picornavirales
Picornaviridae
Hepatovirus
Hepatovirus ahepa
|
HAV causes Hepatitis A; it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is two to six weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last eight weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain.
|
Detail
|
 Hepatitis C Virus
(HCV) Hepatitis C Virus
(HCV)
M
|
9.6kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Hepacivirus
Hepacivirus hominis
|
HCV is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans.
|
Detail
|
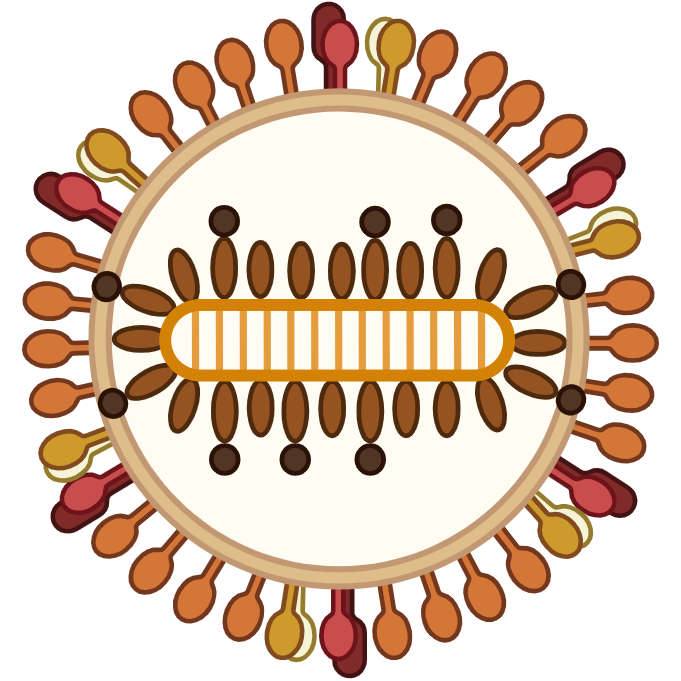 Hepatitis D Virus
(HDV) Hepatitis D Virus
(HDV)
M
|
1.7kb
|
Riboviria
Bunyavirales
Kolmioviridae
Deltavirus
Hepatitis delta virus
|
HDV is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
|
Detail
|
 Hepatitis E Virus
(HEV) Hepatitis E Virus
(HEV)
M
|
7.2kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Hepelivirales
Hepeviridae
Paslahepevirus
Paslahepevirus balayani
|
HEV is the causative agent of hepatitis E. Globally, approximately 939 million corresponding to 1 in 8 individuals have ever experienced HEV infection. About 15–110 million individuals have recent or ongoing HEV infection. The virus particle was first seen in 1983, but was only molecularly cloned in 1989.
|
Detail
|
 Dengue Virus
(DENV) Dengue Virus
(DENV)
M
|
11kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Flavivirus
Orthoflavivirus denguei
|
DENV Dengue virus (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae; genus Flavivirus. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, and a reported fifth has yet to be confirmed, all of which can cause the full spectrum of disease.
|
Detail
|
 Yellow Fever Virus
(YFV) Yellow Fever Virus
(YFV)
M
|
11kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Flavivirus
Yellow fever virus
|
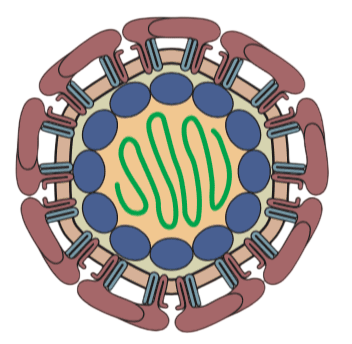
YFV is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains-particularly in the back and headaches.
|
Detail
|
 Japanese Encephalitis Virus
(JEV) Japanese Encephalitis Virus
(JEV)
M
|
11kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Flavivirus
Orthoflavivirus japonicum
|
JEV is a virus from the family Flaviviridae, part of the Japanese encephalitis serocomplex of nine genetically and antigenically related viruses, some of which are particularly severe in horses, and four of which, including West Nile virus, are known to infect humans. JEV is generally spread by mosquitoes, specifically those of the Culex type.
|
Detail
|
 Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus
(TBEV) Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus
(TBEV)
M
|
11kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Flavivirus
Orthoflavivirus encephalitidis
|
TBEV is a positive-strand RNA virus associated with tick-borne encephalitis in the genus Flavivirus.
|
Detail
|
 Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus
(CCHFV) Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus
(CCHFV)
M
|
19-20kb
|
Negarnaviricota
Hareavirales
Nairoviridae
Orthonairovirus
Orthonairovirus haemorrhagiae
|
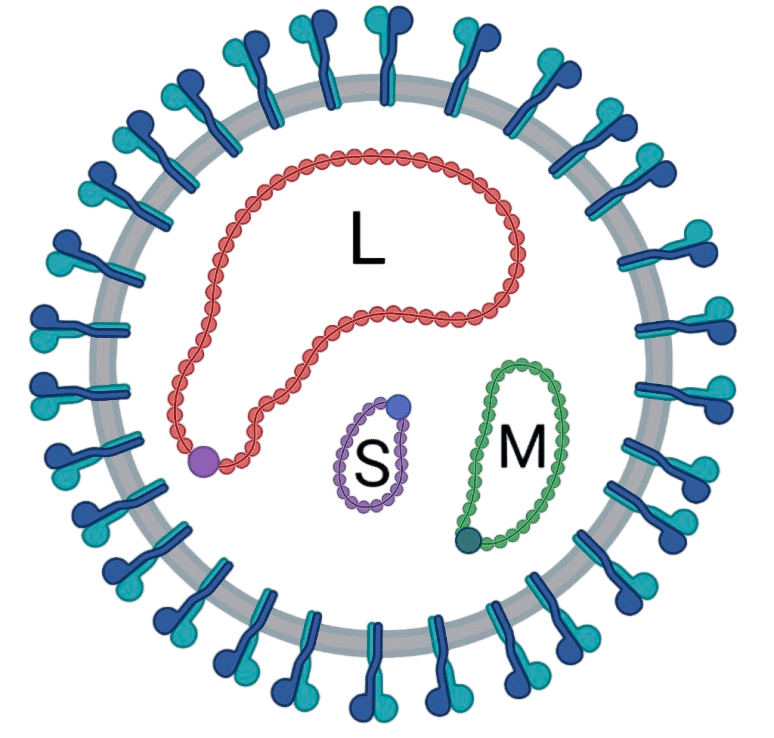
CCHFV is a viral disease. Symptoms of CCHF may include fever, muscle pains, headache, vomiting due to loss of net saline of basal cells, diarrhea, and bleeding into the skin. Onset of symptoms is less than two weeks following exposure. Complications may include liver failure.
|
Detail
|
 Chikungunya Virus
(CHIKV) Chikungunya Virus
(CHIKV)
M
|
12kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Martellivirales
Togaviridae
Alphavirus
Alphavirus chikungunya
|
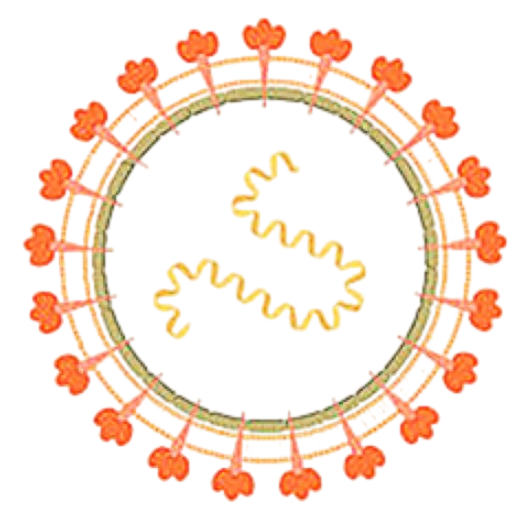
CHIKV is a member of the genus Alphavirus, and family Togaviridae. Chikungunya virus features an icosahedral capsid surrounded by a lipid envelope, with a diameter ranging from 60 to 70 nm. It was first isolated in 1953 in Tanzania and is an RNA virus with a positive-sense single-stranded genome of about 11.6kb. It is a member of the Semliki Forest virus complex and is closely related to Ross River virus, O'nyong'nyong virus, and Semliki Forest virus.
|
Detail
|
 Zika Virus
(ZIKV) Zika Virus
(ZIKV)
M
|
11kb
|
Kitrinoviricota
Amarillovirales
Flaviviridae
Flavivirus
Zika virus
|
ZIKV is a member of the virus family Flaviviridae. It is spread by daytime-active Aedes mosquitoes, such as A. aegypti and A. albopictus. Zika virus shares a genus with the dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and West Nile viruses.
|
Detail
|
 Ebola Virus
(EBOV) Ebola Virus
(EBOV)
M
|
19kb
|
Negarnaviricota
Mononegavirales
Filoviridae
Ebolavirus
Zaire ebolavirus
|
EBOV also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally.
|
Detail
|
 Marburg Virus
(MARV) Marburg Virus
(MARV)
M
|
19kb
|
Negarnaviricota
Mononegavirales
Filoviridae
Marburgvirus
Marburg marburgvirus
|
MARV is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever.
|
Detail
|
 Rabies Virus
(RABV) Rabies Virus
(RABV)
M
|
12kb
|
Negarnaviricota
Mononegavirales
Rhabdoviridae
Lyssavirus
Rabies lyssavirus
|
RABV is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in animals, including humans. It can cause violence, hydrophobia, and fever.
|
Detail
|
 Virus Info Summary
Virus Info Summary